Advanced Cane Sugar Processing: Enhancing Effectiveness and Sustainability
Advanced Cane Sugar Processing: Enhancing Effectiveness and Sustainability
Blog Article
An In-Depth Guide to the Ecological Effect and Sustainability Practices in Walking Cane Sugar Processing
The ecological impact of walking cane sugar processing offers an intricate variety of obstacles that warrant mindful evaluation. From soil degradation and excessive water usage to the carbon footprint associated with cultivation and production, the consequences of standard practices are far-ranging. What particular methods can be applied to strike an equilibrium in between efficiency and environmental stewardship?
Introduction of Cane Sugar Processing
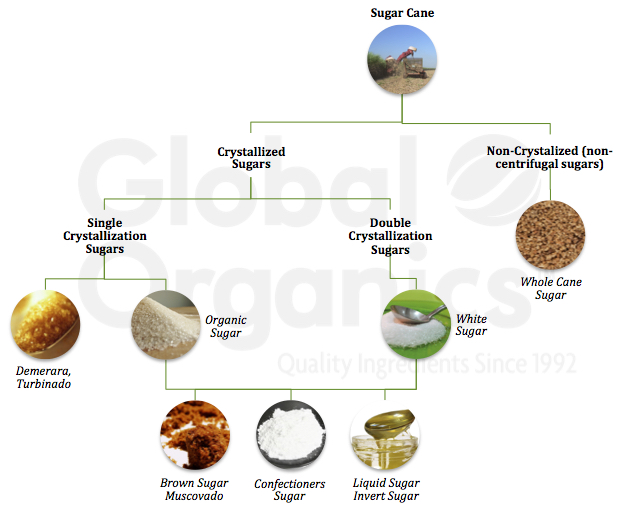
Walking stick sugar handling involves a collection of organized actions that transform sugarcane into refined sugar. Initially, harvested sugarcane is moved to refining centers, where it undergoes cleansing to get rid of dirt and particles. Following this, the walking stick is squashed to extract juice, which is then clarified by getting rid of contaminations with home heating and the addition of lime.
The clarified juice goes through dissipation, where water is gotten rid of to concentrate the sugar content. This concentrated syrup is after that crystallized with air conditioning, permitting sugar crystals to develop. These crystals are divided from the staying syrup utilizing centrifugation, leading to raw sugar. To attain refined sugar, the raw product goes through further filtration processes, which may consist of filtering and cleaning to remove continuing to be pollutants and shade.
The last item is after that dried out and packaged for circulation. Throughout this entire process, preserving effectiveness and quality assurance is important to ensure the sugar meets sector criteria. Each action in walking cane sugar processing not only contributes to the end product but likewise has ramifications for source use and waste generation, setting the phase for conversations on sustainability and environmental effects connected with sugar manufacturing.
Environmental Difficulties of Manufacturing
The manufacturing of cane sugar provides several considerable environmental challenges that warrant attention. One primary problem is the substantial use of agrochemicals, consisting of plant foods and chemicals, which can result in soil destruction, biodiversity loss, and contamination of local water sources. The overflow from sugarcane fields typically carries these chemicals into nearby environments, interfering with water life and affecting the health and wellness of communities reliant on these water bodies.
An additional challenge is the high power consumption related to sugarcane handling. The boiling and refining stages require significant heat, mostly created by burning nonrenewable fuel sources, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. Furthermore, the extensive acreage required for sugarcane cultivation can bring about logging and environment destruction, further intensifying environment change and harmful wild animals.
Moreover, the labor practices in some regions raise honest issues, as workers might face bad working problems and inadequate earnings. This circumstance usually continues a cycle of hardship in local communities. Cane Sugar Processing. Attending to these environmental difficulties is important for creating more sustainable techniques in walking cane sugar production, inevitably profiting both the atmosphere and the neighborhoods associated with this market
Water and Land Use Impact
Water sources and land use are essential parts in the walking cane sugar sector that considerably affect the environment. The cultivation of sugarcane needs considerable water input, with price quotes recommending that it can consume approximately 2,000 litres of water per kilo of sugar generated. This extensive use of water commonly brings about exhaustion of local water resources, impacting not only the sugarcane haciendas but additionally bordering communities and areas that count on the exact same water sources for farming and residential use.
Furthermore, land usage for sugarcane growing can lead to deforestation and the conversion of all-natural habitats right into monoculture vineyards. This method diminishes biodiversity, interferes with regional communities, and adds to dirt deterioration. The expansion of sugarcane areas usually intrudes on valuable helpful hints farming land, creating competition for resources between food and biofuel manufacturing.
Lasting techniques, such as maximizing irrigation techniques and applying plant rotation, are necessary to reduce these effects. By embracing more effective water usage and land management techniques, the walking cane sugar market can decrease its ecological impact, guaranteeing an equilibrium between farming productivity and ecological preservation.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Greenhouse gas discharges stand for a considerable ecological worry within the walking stick sugar handling sector, particularly as agricultural techniques expand to satisfy international demand. The cultivation of sugarcane, a crop that prospers in exotic environments, counts greatly on synthetic plant foods and chemicals, which add to laughing gas emissions. Additionally, land-use modifications, consisting of logging for brand-new sugarcane haciendas, release carbon dioxide stored in vegetation and soil.
During handling, power usage is another significant source of greenhouse gas exhausts - Cane Sugar Processing. Numerous sugar mills use fossil fuels to power equipment and produce heat, resulting in significant carbon impacts. Furthermore, the transport of raw sugarcane and finished products includes layers of emissions via gas burning in lorries
The advancing effect of these discharges intensifies environment modification, presenting risks not only to the atmosphere yet likewise to the long-lasting feasibility of the industry. Stakeholders need to recognize the urgent need for comprehensive approaches that resolve these discharges. This entails evaluating existing farming practices, refining approaches, and transportation systems to determine areas for enhancement and reduction. Addressing greenhouse gas discharges is vital for fostering a more lasting walking stick sugar industry in an altering climate.

Sustainable Practices and Innovations
Sustainable practices and advancements are progressively important in the walking stick sugar handling market as stakeholders seek to lower ecological influences while maintaining productivity. One considerable innovation is the application of integrated plant management, which enhances resource use by incorporating soil management, insect control, and crop rotation strategies. This method boosts yield while decreasing chemical inputs and protecting soil wellness.
Furthermore, the adoption of renewable resource resources, such as biomass from sugarcane residues, has gotten grip - Cane Sugar Processing. By converting waste products right into power, processing centers can reduce their reliance on fossil gas, thus reducing greenhouse gas emissions
Water monitoring methods have actually also seen enhancements with the recycling and reusing of water in processing plants, considerably lowering freshwater usage. Advancements in modern technology, such as precision agriculture, allow farmers to monitor crop health and wellness and resource use more home efficiently, making sure lasting cultivation techniques.
In addition, qualification programs like Fair Trade and Jungle Partnership encourage eco accountable farming practices and promote social equity within the supply chain. By embracing these lasting practices and developments, the cane sugar handling industry can boost its durability and add positively to ecological stewardship.
Final Thought
The environmental effect of walking stick sugar processing offers substantial obstacles, including soil have a peek at this site deterioration, high water usage, and greenhouse gas discharges, together with honest issues connected to labor practices. Dealing with these issues through sustainable techniques, such as incorporated crop management, renewable resource adoption, and water recycling, is necessary. By promoting environmentally responsible and socially fair methods in sugar manufacturing, the market can reduce its adverse results, making certain a much more sustainable future for both communities and communities involved in this sector.
Walking cane sugar processing involves a collection of methodical actions that change sugarcane into polished sugar. Each step in walking cane sugar processing not only adds to the final item however also has effects for resource usage and waste generation, setting the phase for discussions on sustainability and ecological effects linked with sugar production.
Greenhouse gas exhausts represent a substantial environmental concern within the walking stick sugar processing market, particularly as farming practices increase to meet international demand.Sustainable techniques and developments are increasingly crucial in the cane sugar handling industry as stakeholders seek to decrease ecological impacts while maintaining productivity.The environmental impact of cane sugar handling presents substantial challenges, including dirt deterioration, high water intake, and greenhouse gas emissions, together with moral issues associated to labor techniques.
Report this page